How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill increasingly sought after, opening doors to breathtaking aerial photography, insightful inspections, and even recreational fun. This guide provides a structured approach, from pre-flight checks and essential controls to advanced techniques and legal considerations. We’ll cover everything you need to know to confidently take to the skies, ensuring both a smooth flight and responsible operation.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource to begin your journey is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. From pre-flight checks to mastering maneuvers, proper training ensures safe and effective drone operation.
Mastering drone operation involves understanding not only the mechanics of flight but also the crucial aspects of safety, legality, and ethical considerations. From initial setup and pre-flight checks to navigating different flight modes and handling emergencies, we will explore each step in detail, equipping you with the knowledge and confidence to become a proficient drone pilot.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is crucial for safe and responsible drone operation. It minimizes risks and ensures optimal flight performance. This involves a systematic inspection of the drone and its components, as well as understanding and adhering to relevant safety guidelines.
Pre-Flight Inspection Steps
Before each flight, perform a comprehensive inspection. This includes checking the battery level, examining the propellers for damage, and verifying a strong GPS signal.
| Check Item | Procedure | Acceptable Result | Unacceptable Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery Level | Check the battery indicator on the drone and/or remote controller. | Battery level above 20%, ideally above 50%. | Battery level below 20%; replace or recharge. |
| Propeller Condition | Visually inspect each propeller for cracks, chips, or bends. | Propellers are undamaged and securely attached. | Damaged propellers; replace before flight. |
| GPS Signal | Power on the drone and observe the GPS indicator. | Solid GPS signal with sufficient satellites locked. | Weak or no GPS signal; wait for a stronger signal or find a more open location. |
| Gimbal Calibration (if applicable) | Follow manufacturer’s instructions to calibrate the gimbal. | Gimbal moves smoothly and accurately. | Gimbal is not calibrated correctly; recalibrate or seek assistance. |
Drone Safety Guidelines
Operating a drone safely requires awareness of airspace restrictions and adherence to emergency procedures. Understanding and complying with local regulations is paramount.
- Always check for and respect airspace restrictions. Many areas prohibit drone flights near airports, military bases, or other sensitive locations.
- Maintain visual line of sight with your drone at all times. Do not fly beyond your visual range.
- Be aware of your surroundings and avoid flying near people, animals, or obstacles.
- Never fly your drone in inclement weather such as strong winds, rain, or snow.
- In case of an emergency, immediately attempt a safe landing procedure. If the drone becomes unresponsive, initiate the return-to-home function (if available).
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation: How To Operate A Drone
Understanding the basic controls and navigation methods is essential for safe and effective drone operation. This includes mastering the various flight modes and selecting the appropriate navigation technique for the task at hand.
Basic Drone Controls
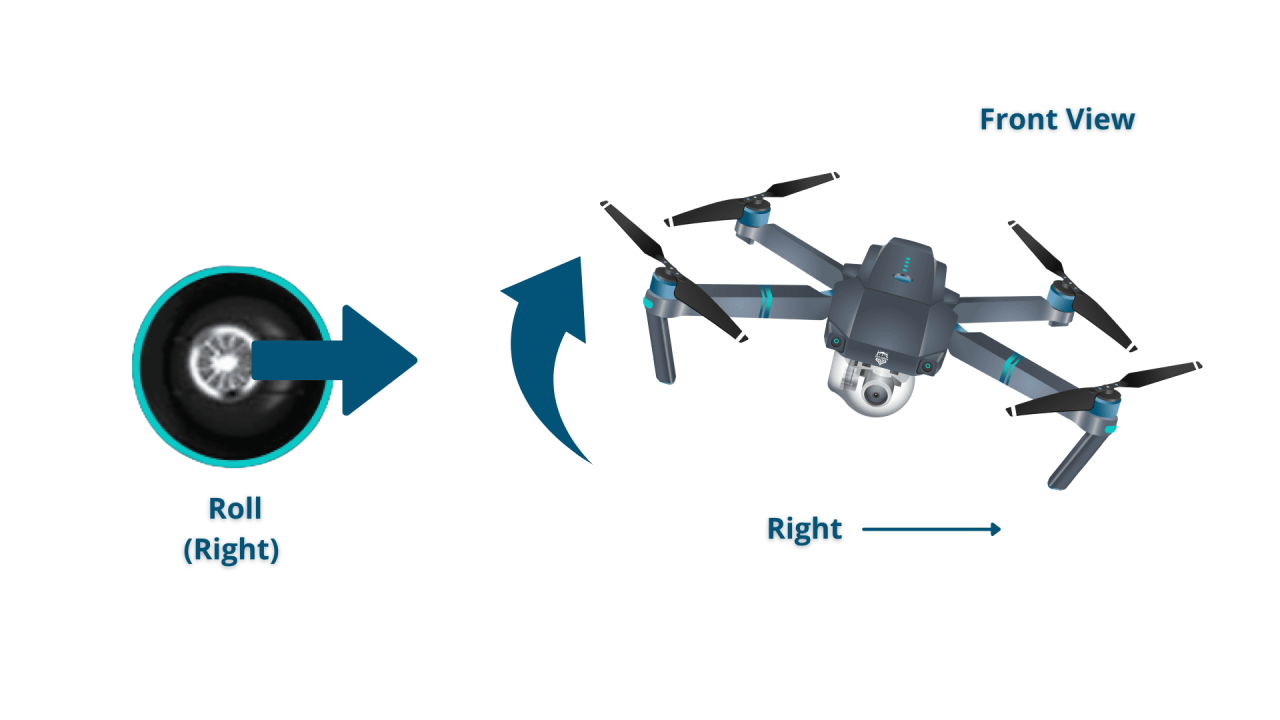
Most drones use a controller with sticks that control throttle, yaw, pitch, and roll. Throttle controls altitude, yaw controls rotation, pitch controls forward/backward movement, and roll controls left/right movement. Understanding these controls is fundamental to piloting.
Flight Modes and Applications
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and stability. Common modes include Attitude mode (for beginners), GPS mode (for stable hovering and autonomous flight), and Sport mode (for more agile maneuvers). Choosing the appropriate mode depends on your skill level and the task at hand.
Drone Navigation Methods
GPS-based navigation provides stable and precise control, especially helpful for beginners. Manual control offers greater precision but requires more skill and practice. Hybrid approaches, combining GPS and manual input, are also common.
Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
- Power on the drone and controller, ensuring a strong GPS signal.
- Calibrate the drone’s compass according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Gently increase the throttle to lift off. The drone should ascend vertically.
- Practice hovering by making small adjustments to the throttle and directional controls.
- To land, slowly lower the throttle until the drone gently touches down.
Mastering Drone Flight Techniques
Smooth and controlled maneuvers require practice and understanding of various flight techniques. This includes adapting to challenging conditions and avoiding common mistakes.
Smooth and Controlled Maneuvers
Practice slow, deliberate movements to gain control. Avoid sudden inputs and jerky movements. Focus on maintaining a stable altitude and orientation.
Flying in Windy Conditions
Wind can significantly impact drone stability. Choose calm days for flying whenever possible. If wind is present, fly into the wind during takeoff and landing for better control. Reduce speed and use more precise control inputs.
Common Mistakes and Solutions
Common mistakes include losing visual line of sight, flying too close to obstacles, and neglecting battery life. Maintaining awareness, practicing safe flying habits, and monitoring battery levels are crucial to avoiding these errors.
Advanced Flight Techniques
Advanced techniques include aerial photography maneuvers such as orbiting, tracking, and cinematic shots. These require a higher level of skill and practice but significantly enhance the quality of your aerial footage.
Learning to operate a drone involves understanding its controls and safety procedures. A crucial step is familiarizing yourself with the basics, which can be easily achieved by consulting a comprehensive guide, such as the one found here: how to operate a drone. This resource provides valuable insights into various aspects of drone operation, ensuring a safe and efficient flying experience.
Proper understanding of how to operate a drone is paramount for responsible and enjoyable use.
Drone Photography and Videography
Achieving high-quality aerial photography and videography involves understanding camera settings, composition, and drone features.
Adjusting Camera Settings
Camera settings like ISO, shutter speed, and aperture affect image quality in different lighting conditions. Adjust these settings based on the amount of available light. Higher ISO is needed in low light, but this increases noise. A faster shutter speed helps freeze motion, while a slower speed can create motion blur.
Composing Compelling Aerial Shots
Consider the rule of thirds, leading lines, and the overall visual balance when composing shots. Experiment with different angles and perspectives to capture unique and captivating images.
Using Drone Features

Zoom and gimbal control are valuable tools for enhancing footage. Zoom allows you to get closer to your subject, while gimbal control stabilizes the camera and allows for smooth shots even during flight maneuvers.
Shot Types and Camera Settings
| Shot Type | Camera Settings (Example) | Drone Maneuvers |
|---|---|---|
| Wide Shot | Wide angle lens, low ISO, appropriate shutter speed | High altitude, slow, steady movement |
| Close-up | Telephoto lens, higher ISO (if needed), appropriate shutter speed | Lower altitude, precise movements, gimbal control |
| Tracking Shot | Appropriate lens, consistent shutter speed, smooth gimbal movement | Following a subject at a consistent distance and speed |
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Drone operation is subject to various legal requirements and regulations that vary by region. Understanding and adhering to these regulations is crucial for avoiding penalties and ensuring safe operation.
Legal Requirements and Regulations
Regulations often cover areas such as registration, airspace restrictions, and operational limitations. These regulations are designed to ensure safety and prevent misuse of drones.
Drone Registration
Many regions require drone registration with the relevant authorities. Registration typically involves providing information about the drone and its owner. This helps track drones and hold owners accountable.
Airspace Restrictions
Airspace restrictions often prohibit drone flights near airports, military bases, and other sensitive locations. Checking for and respecting these restrictions is essential.
Penalties for Violations
Violating drone regulations can result in fines, legal action, and even drone confiscation. Understanding and complying with the regulations is crucial to avoid these consequences.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are crucial for extending the lifespan of your drone and ensuring its reliable performance.
Routine Drone Maintenance
This includes cleaning the drone’s body and propellers, inspecting for damage, and properly storing the drone and its components. Regular battery care, including proper charging and storage, is also essential.
Troubleshooting Common Problems
Common issues include battery problems, motor malfunctions, and GPS signal loss. Understanding the causes and solutions for these problems can prevent costly repairs or replacements.
Proper Drone Storage
Storing the drone in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and moisture, helps prevent damage and extends its lifespan.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions, How to operate a drone
- Problem: Low battery warning. Solution: Land immediately and recharge the battery.
- Problem: Motor malfunction. Solution: Inspect the motor for damage and replace if necessary.
- Problem: GPS signal loss. Solution: Move to an area with a clear view of the sky and restart the drone.
Emergency Procedures and Safe Landing
Knowing how to handle unexpected situations and perform a safe emergency landing is critical for safe drone operation. This includes understanding procedures for low battery warnings, signal loss, and other emergencies.
Handling Unexpected Situations
Low battery warnings require immediate action to avoid a sudden power failure. Loss of signal requires immediate action to prevent loss of control and potential damage. Understanding the drone’s return-to-home function is important.
Safe Emergency Landing

A safe emergency landing involves gradually lowering the throttle while maintaining control of the drone’s orientation. Choose a safe landing area, clear of obstacles and people.
Recovering a Drone After a Crash
Inspect the drone for damage, repair or replace damaged components, and recalibrate the drone if necessary. Follow manufacturer instructions for any specific post-crash procedures.
Emergency Scenarios and Responses
- Scenario: Low battery warning. Response: Initiate immediate return-to-home and land the drone safely.
- Scenario: Loss of signal. Response: Attempt to regain signal. If unsuccessful, initiate return-to-home if available, otherwise perform a controlled emergency landing.
- Scenario: Unexpected strong winds. Response: Land the drone immediately and wait for calmer conditions.
Understanding Drone Batteries and Charging
Proper battery care is essential for safe and efficient drone operation. This involves understanding battery types, safe charging practices, and recognizing signs of battery damage.
Using the Correct Battery
Always use the battery specifically designed for your drone model. Using an incorrect battery can lead to malfunctions, damage, or even fire.
Safe Charging Practices
Charge batteries in a well-ventilated area, away from flammable materials. Never leave batteries unattended during charging. Use the recommended charger and follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
Signs of Damaged Battery
Signs of damage include swelling, leaking, or unusual odors. Never use a damaged battery. Dispose of damaged batteries properly according to local regulations.
Battery Types, Charging Times, and Flight Times
| Battery Type | Charging Time (Example) | Flight Time (Example) |
|---|---|---|
| LiPo 3S 1500mAh | 60-90 minutes | 15-20 minutes |
| LiPo 4S 2200mAh | 90-120 minutes | 25-30 minutes |
Successfully operating a drone requires a blend of technical understanding and responsible piloting. By diligently following pre-flight procedures, mastering the controls, and adhering to legal regulations, you can unlock the vast potential of aerial technology. Remember that continuous practice and a commitment to safety are key to becoming a skilled and responsible drone operator.
Enjoy the journey and the stunning perspectives that await!
Question & Answer Hub
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS stabilization and automated features are ideal for beginners. Look for models with intuitive controls and obstacle avoidance capabilities.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Compass calibration should be performed before each flight, especially if the drone has been moved significantly or exposed to magnetic interference.
What should I do if I lose signal with my drone?
Most drones have a “return-to-home” (RTH) function. Activate this immediately. If unavailable, attempt to regain signal while carefully guiding the drone downwards for a safe landing.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model and flight conditions. Check your drone’s specifications for estimated flight times; expect shorter flight times in windy conditions or when using high-power features.
What is the best way to clean my drone?
Use a soft, dry cloth to gently wipe away dirt and debris. Avoid using water or harsh chemicals unless specifically recommended by the manufacturer.
